Historic Engineering Marvel: Exploring the Structural Wonders of the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China, an iconic symbol of Chinese civilisation, stands as one of the most remarkable architectural feats in human history. Stretching for thousands of miles across rugged terrain, this ancient structure is a testament to the ingenuity, perseverance, and engineering prowess of ancient Chinese builders. In this blog post, we will delve into the structural wonders of the Great Wall of China, exploring its historical significance, construction techniques, and enduring legacy.
Contents |
[edit] A Brief History of the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China is not a single, continuous wall but rather a series of fortifications built over centuries to protect the Chinese Empire from invasions. Construction began during the Qin Dynasty (221-206 BCE), when Emperor Qin Shi Huang ordered the unification of existing walls along the northern frontier. Over the following centuries, various dynasties expanded and repaired the wall, resulting in a complex and multifaceted structure.
[edit] The Structural Marvels of the Great Wall
The Great Wall's construction is a testament to ancient Chinese engineering ingenuity. The wall's sections vary in width and height depending on the terrain and defensive needs. In some areas, the wall is wide enough to accommodate multiple layers of troops and equipment. The wall's foundation is typically made of stone or packed earth, providing a solid base for the superstructure. The above-ground portions of the wall are often constructed of rammed earth, a mixture of soil, water, and other materials that is compacted into layers to form a durable structure.
One of the most impressive features of the Great Wall is its system of watchtowers. These strategically placed towers served as observation posts, allowing soldiers to monitor the surrounding countryside and detect potential threats. The watchtowers are often multi-story structures with crenellated walls and lookout platforms. Some towers also included living quarters for soldiers and storage facilities.
[edit] The Challenges of Construction
Building the Great Wall was a monumental undertaking, fraught with challenges. The construction process required a massive workforce, and labourers often faced harsh conditions, including extreme weather, difficult terrain, and the threat of enemy attacks. The transportation of materials, such as stones and timber, over long distances was another significant challenge. Despite these obstacles, the ancient Chinese builders succeeded in creating a structure that has endured for centuries.
[edit] The Great Wall's Enduring Legacy
Today, the Great Wall of China is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a popular tourist destination. It serves as a symbol of Chinese history, culture, and resilience. The wall's construction techniques and architectural features continue to inspire engineers and architects around the world.
In conclusion, the Great Wall of China is a truly remarkable engineering marvel. Its construction represents a testament to the ingenuity, perseverance, and skill of ancient Chinese builders. The wall's enduring legacy serves as a reminder of the power of human ingenuity and the importance of preserving our cultural heritage.
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
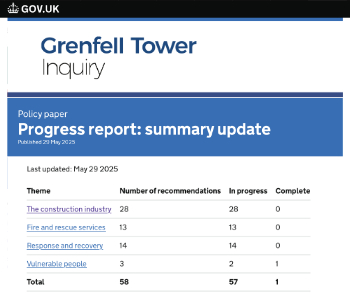
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.